Ball valves are indispensable components in piping systems, serving as reliable on/off controls for liquids or gases. However, achieving proper functionality requires an understanding of ball valve flow direction. This article serves as a comprehensive guide to ensure you understand the nuances of ball valve direction, including unidirectional and bidirectional valves, proper installation techniques, and their impact on system efficiency.
Do Ball Valves Have a Flow Direction?
Yes, ball valves can have a specified flow direction, depending on their type. This is particularly important when working with unidirectional ball valves, which allow flow only in one direction. On the other hand, most modern ball valves are bidirectional, making them more versatile for various applications.
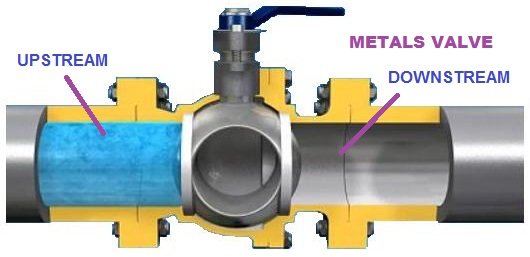
Understanding flow direction is crucial to ensure your valve operates efficiently and prevents operational errors, such as leaks or disruptions downstream. It is especially important in industries like chemical processing or pharmaceuticals, where precision matters.
Unidirectional vs. Bidirectional Ball Valves
Unidirectional Ball Valves
Unidirectional ball valves allow flow in one direction only. Their design includes a single-seat mechanism that creates a tight seal, effectively preventing backflow. This flow direction is usually indicated by an arrow displayed on the valve body.
- Applications: Systems requiring backflow prevention, such as water supply pipelines or chemical processes.
- Examples:
-
- C Ball Valves and V Port Ball Valves are specialized for controlling single-direction flow.
- Orbit Ball Valves commonly used in safety-critical applications.
- What to know:
-
- You must install these valves in the direction of the flow indicated by the marking or arrow on the valve body to prevent system inefficiencies.
Bidirectional Ball Valves
Bidirectional ball valves, also known as two-way ball valves, allow flow in either direction. These valves feature double-seated designs, which enable them to seal tightly regardless of the flow’s direction.
- Applications: General-purpose systems in plumbing, HVAC, and fluid flow pipelines.
- Benefits:
-
- Flexible installation, as their performance is unaffected by how they are plumbed.
- Ideal for systems requiring equal performance upstream and downstream.
- Common Types:
-
- Gate Valves, which allow shut-off in either direction.
- Cryogenic Ball Valves, designed for low-temperature applications.
How to Determine the Direction of Flow in Ball Valves
To identify the correct direction of flow for a ball valve, follow these guidelines:
- Check the Arrow Marking:
-
-
- For unidirectional ball valves, look for an arrow engraved or printed on the valve body. This arrow indicates the correct flow direction from the inlet to the outlet.
-
- Inspect the Handle Position:
-
-
- The handle on most ball valves aligns with the flow direction when the valve is open.
- Example: If the handle points parallel to the pipe, the valve is likely open and aligns with the medium’s flow.
-
- Review Manufacturer’s Documentation:
-
-
- Consult the installation manuals or datasheets, which often detail the correct orientation for installation based on the valve type.
-
- Examine Internal Design:
-
-
- Certain valves require a visual inspection of their internal design to confirm the flow path. For example, unidirectional valves typically have more intricate seat structures aligned for single flow.
-
- Look for Additional Indicators:
-
-
- Some ball valves are equipped with written labels or textual markings on their bodies that specify flow direction.
-
Unidirectional Ball Valves: Key Features and Installations
Unidirectional ball valves are integral to preventing backflow and maintaining system integrity. Proper installation is critical, as incorrect orientation can lead to inefficiencies or equipment damage.
Tips for Installation:
- Ensure the valve’s arrow points toward the system’s downstream direction.
- Use tools like Teflon tape when threading the valve for a secure fit.
- Align the valve properly to eliminate leaks or operational inefficiencies.
Close Direction in Unidirectional Valves
When closing a unidirectional valve:
- Turn the lever clockwise until the handle aligns perpendicular to the flow.
- This creates a tight seal, stopping the system’s medium entirely.
Bidirectional Ball Valves: Benefits in Versatile Applications
Bidirectional valves provide unmatched flexibility and ease of installation, as no specific flow alignment is required.
Why Choose Bidirectional Valves?
- Flexible Operations:
-
- Handles flow in either the upstream or downstream direction.
- User-Friendly Installation:
-
- Eliminates confusion regarding orientation during plumbing or maintenance tasks.
- Durability:
-
- Often feature double-seated designs, ensuring tight seals across both flow directions.
Plumbing Ball Valves Correctly with Directional Markings
Proper plumbing ensures optimal valve efficiency. Here are the steps to plumb your ball valves correctly:
- Use the manufacturer-provided arrow marking to orient unidirectional valves.
- For bidirectional valves, ensure the valve is securely fastened without over-tightening connections.
- Test for leaks by running water or the medium through the valve, watching for excessive pressure or misalignment in connections.
How Ball Valve Flow Direction Impacts Plumbing Systems
The flow direction of ball valves plays a significant role in maintaining the overall performance and durability of the plumbing system.
Key Points to Consider:
- System Efficiency:
-
- Correct installation minimizes energy losses and ensures optimal medium flow rates.
- Safety:
-
- Proper directionality prevents accidental backflow, reducing potential hazards.
- Longevity:
-
- Incorrectly oriented valves can expose internal components to undue stress, shortening their lifespan.
Ball Valves for Your Business
Selecting the right type of ball valve for your system comes down to understanding the flow requirements specific to your application.
Factors to Consider:
- Flow direction requirements (unidirectional vs. bidirectional).
- System pressure and temperature.
- Material type (e.g., brass, stainless steel).
- Manufacturer’s recommendations specific to your industry.
For example:
- A high-pressure system in a chemical plant might require unidirectional forged ball valves, while a plumbing setup could benefit from bidirectional two-way valves for ease of use.
Final Thoughts on Ball Valve Flow Direction
Ensuring the correct ball valve flow direction is essential for efficient system operation, safety, and longevity. By understanding whether your system requires unidirectional or bidirectional valves and paying close attention to installation markings, you can avoid leaks, inefficiencies, and costly repairs.
When choosing the right valves for your business, ensure they align with your system’s needs and consult manufacturer documentation where needed. Proper valve function begins with proper installation.
Don’t leave room for error in flow direction! Examine your system’s requirements and always opt for high-quality valves from trusted manufacturers to get the job done right.