Butterfly Valve vs. Ball Valve is a popular topic when it comes to the factor of fluid control. These types of valves are widely used in industries to control the flow of liquids and sometimes gases, but they work differently in design, cost, and functions. Therefore, based on the advantages, disadvantages, size, cost, price, and the application of the valves, the right one needs to be chosen.
This guide shows you the main differences between butterfly valves and ball valves to help you pick the right one for your system. We will examine both valve types to provide every detail you require to make the right decision.
Overview of Butterfly Valves and Ball Valves
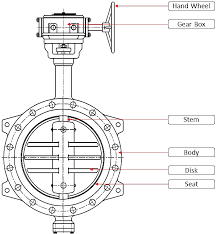
What Is a Butterfly Valve?
A butterfly valve works by turning 90 degrees to let or block fluid movement through a rotating flat piece. A rotary valve disc rotates on its centre point to allow or deny fluids or gas movement through the valve. Butterfly valves work efficiently in large-diameter flow control systems because they offer both low-price and light bodies.
Key Features of Butterfly Valves:
Operation: The moving disc goes through a complete 90-degree turn to switch flow direction.
Design: The valve design includes a narrow profile that fits easily into confined areas.
Versatility: Available in various materials, suitable for low to medium pressure and temperature systems.
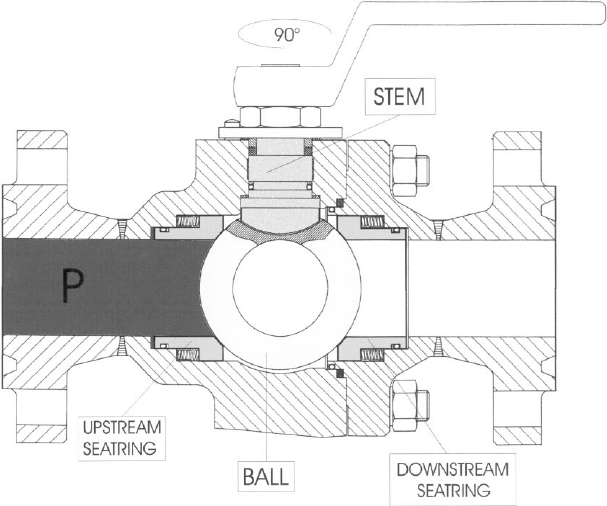
What Is a Ball Valve?
A ball valve is also a quarter-turn valve, using a spherical ball with a hole (bore) drilled through it to manage flow. Moving the ball valve in the line direction creates a pipeline opening while turning it 90 degrees seals the passage. People value ball valves as tight-sealing components built for demanding high-pressure tasks.
Key Features of Ball Valves:
Sealing: Closings with a ball valve deliver perfect flow blockage under tough working environments.
Durability: Performs well in high-pressure and high-temperature environments.
Minimal Pressure Drop: The system opens freely without pressure loss to the pipeline.
Butterfly Valve vs Ball Valve: Key Differences
1. Design and Mechanism
Butterfly Valve: It has a disc that rotates in the flow path even when it is fully open.
Ball Valve: It has a spherical ball with a bore, which, when turned, opens the valve and does not hinder the flow of the fluid.
2. Size and Weight
Butterfly Valve: Lightweight and compact, ideal for large-diameter pipelines.
Ball Valve: Heavier and bulkier, particularly in larger sizes.
3. Flow and Pressure Control
Butterfly Valve: Its main disadvantage is that it results in a slight pressure drop since the disc sits within the flow stream.
Ball Valve: Ensures minimal pressure loss and smooth flow.
4. Cost and Price
Butterfly Valve: More affordable, especially for larger diameters.
Ball Valve: This valve has a higher initial cost but is suitable for more use and abuse than any other valve type.
5. Sealing Efficiency
Butterfly Valve: Adequate for general applications but less effective for absolute leak prevention.
Ball Valve: Gives a good shut-off, making it suitable for most critical operations.
6. Maintenance
Butterfly Valve: Requires regular maintenance, particularly for seals and discs.
Ball Valve: Durable with minimal maintenance needs.
To understand the working principles better, here are visual representations of the two valves:
Butterfly Valve and Ball Valve Working Principles
Left: Butterfly Valve uses a rotating disc. Right: ball valve uses a spherical ball to regulate flow.
Butterfly Valve vs Ball Valve: Key Differences
| Parameter | Butterfly Valve | Ball Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Rotating disc obstructs flow even when fully open | Spherical ball offers unobstructed flow |
| Size & Weight | Lightweight, compact, suitable for large diameters | Heavier, bulkier, especially in larger sizes |
| Flow Control | Moderate, some turbulence due to disc interference | Excellent, minimal pressure drop |
| Cost | More affordable, especially for larger sizes | Higher initial cost but durable for long-term use |
| Sealing Efficiency | Adequate for most applications | Superior sealing for critical operations |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance, especially for seals | Minimal maintenance, long-lasting |
Butterfly Valve vs Ball Valve Pros and Cons
Pros of Butterfly Valves:
Cost-Effective: Butterfly valves are low-cost, especially large valves in large-diameter pipeline systems.
Lightweight Design: It is easy to transport and install, especially in areas that have limited space.
Ease of Operation: A quarter-turn actuation allows the fast operation of the flow control.
Wide Range of Sizes: Suitable for pipelines of various diameters.
Cons of Butterfly Valves:
Limited Tight Sealing: It is not very suitable when there is a possibility of oil leakage.
Pressure loss: As shown in the flow path diagram, there is a disc that will create turbulence.
Vibration Issues: Due to the increase in the flow rate, vibrations occur at the disc.
Pros of Ball Valves:
Superior Sealing: Provides a leak-proof solution, even under high pressure.
Durability: The system is able to endure different environments, such as hot temperatures and corrosive metals and fluids.
Low Operating Pressure: It does not obstruct the flow while offering the least pressure loss.
Uses: The Cartesian control can be used as an on-off controller that can also be used as a flow controller.
Cons of Ball Valves:
Higher Cost: Ball valves are comparatively expensive compared to other types of valves.
Requires More Space: This is because the device is relatively big and bulkier than other modern gaming devices.
Aging: Surfaces to be sealed may wear off with abrasive media over specific periods.
Fluid Dynamics Comparison
- Butterfly Valve:
The disc remains in the fluid path even when fully open, causing turbulence and pressure drop. This makes butterfly valves suitable for low-pressure systems like HVAC or water pipelines but less ideal for high-pressure demands. - Ball Valve:
Ball valves, when fully open, provide an unobstructed flow path, resulting in minimal pressure drop. However, partially opened states can lead to erosion of the ball surface, especially with abrasive or corrosive fluids.
Applications of Butterfly Valves and Ball Valves
Common Applications of Butterfly Valves:
- Water Management: Used in pipelines for municipal water systems.
- HVAC Systems: Regulates airflow in heating and cooling systems.
- Chemical Processing: Suitable for low-pressure applications.
- Food and Beverage: Ensures sanitary flow control.
Common Applications of Ball Valves:
- Oil and Gas: Ideal for high-pressure pipeline systems.
- Power Plants: Handles steam and condensate systems efficiently.
- Pharmaceuticals: Provides reliable sealing for sensitive chemicals.
- Marine Systems: Performs well in saltwater and harsh environments.
Butterfly Valve vs Ball Valve: Cost Comparison
A butterfly valve is relatively cheaper than the ball valve regardless of the material of construction, although the cost difference may vary with the specific type of butterfly valve in question.
The butterfly valves and ball valves differ in their cost. We have to consider the sizes, materials, and pressure of the two kinds. Generally:
Butterfly Valves: More affordable, especially for larger sizes.
Ball Valves: Comparatively expensive at the initial stage but ideal for use in the long run.
For example:
Butterfly valves of the same size as the 6-inch price between $200-$400, whereas ball valves of the same size are priced between $500-$800.
Decision Tree for Valve Selection
To simplify the selection process:
Butterfly Valve vs Ball Valve: How to Choose?
- **Need lower cost and compact design?** → Choose a Butterfly Valve
- **Need high sealing performance for high-pressure or high-temperature systems?** → Choose a Ball Valve
- **Handling corrosive or abrasive fluids?**
- On a budget → Choose a Lined Butterfly Valve
- Flexible budget → Choose a Corrosion-resistant Ball Valve
- **Need minimal maintenance and long lifespan?** → Choose a Ball Valve
Industry Standards for Butterfly and Ball Valves
When selecting between butterfly and ball valves, compliance with industry standards is essential. Some key standards include:
- API 609: Governs butterfly valves for industrial use.
- API 608: Specifies ball valve requirements for piping systems.
- ASME B16.34: Covers valve pressure-temperature ratings and materials.
Refer to resources like Valve World for detailed technical insights.
Key Takeaways: Butterfly Valve vs Ball Valve
The selection between butterfly valves and ball valves is based on your application requirement. To summarize:
Choose a Butterfly Valve If:
Besides the cost of the product, space-saving is the other priority.
It has medium pressure and temperature control requirements.
Choose a ball valve if:
Critical is tight sealing and durability.
The system contains the high pressure, temperature, or corrosive materials.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can Butterfly Valves Be Used for High-Pressure Systems?
In medium pressure systems, butterfly valves function better, whereas ball valves find application in high pressure systems.
2. Which Valve Is More Durable?
Ball valves are especially more durable in extreme conditions.
3. What makes ball valves more expensive?
However, ball valves are more expensive due to their construction and the superior sealing performance.
4. Do Butterfly Valves Have the Ability to Handle Corrosive Fluids?
It would, of course, yes, as long as it is lined with corrosion-resistant materials such as PTFE.
Explore Related Topics
Want to learn more about valves? Check out:
- Gate Valve vs Globe Valve: Key Differences
- How to Choose the Right Valve Material
- Top 5 Tips for Valve Maintenance
Future Trends in Valve Technology
Smart Valves:
Power supply using electric butterfly and ball valves with Internet of Things (IoT)-equipped actuators for tracking and management.
Smart ball valves with sensors for real-time data collection (flow rate, pressure, temperature).
Advanced Materials:
Composite materials (e.g., carbon fibre) for lighter, more corrosion-resistant butterfly valves.
Super StringField applications include subsea-liquefied natural gas, nuclear power plants, and other kinds of industries.
Energy Efficiency:
By a suitable investment design for the butterfly valves, pressure drop can be reduced.
Ball valves with enhanced sealing mechanisms will reduce the chances of leakage to a great extent.
Conclusion
Butterfly valves and ball valves are two different types of valves that are used in an industry; depending on certain factors such as application, cost, and specifications, one needs to prefer one. When it comes to choosing between either of them, there are vital variations that you need to be familiar with, as well as both their advantages and disadvantages. By comparing the differences and advantages and disadvantages, you can ensure performance and cost factors that will guarantee the success of the enterprise.